




Join the ALPD: Internal Investigations Unit and solve the case of hypophosphatasia (HPP) before it can potentially cause more harm to your patients.
Be on the lookout for low alkaline phosphatase (ALP).







Sign up for the latest news and information about hypophosphatasia and/or be connected with your local Alexion representative.
*Indicates required field.
You're one step closer to catching HPP! Keep your eyes peeled for more news and information.

Compare your patient’s current and historical ALP levels from their comprehensive metabolic panel against normal age- and sex-adjusted reference ranges.
Based on the age- and sex-adjusted reference range4-8
ALP Activity (U/L)
null



100
100
High = over 369 U/L
Normal = 156-369 U/L
Low = under 156 U/L
Limitations: A low ALP value is not conclusive for diagnosis of HPP. Patient should be evaluated for other symptoms of HPP and differential diagnoses should be ruled out. Check with your lab for their appropriate age- and sex- adjusted reference ranges.7
Persistently low age- and sex-adjusted ALP is the biochemical hallmark of HPP.1,2 Paired with key signs and symptoms, persistently low ALP can confirm a diagnosis of HPP. Be sure to check your patient’s prior comprehensive metabolic panel results to assess historical ALP levels.1-3

After reviewing this information, how confident are you in considering a diagnosis of HPP in patients with perplexing symptoms and persistently low age- and sex-adjusted ALP?
NOTE: Reference range was taken from the Canadian Laboratory Initiative on Pediatric Reference Intervals (CALIPER) Database which compiled age- and sex-specific reference intervals in a pediatric population.3
*Clinicians should ensure that reported laboratory results for ALP reflect age- and sex-adjusted reference ranges for the specific patient.
Check with your lab for their appropriate age- and sex- adjusted reference range.
This resource is for educational purposes only. It is not intended for use in diagnosis of any disease or condition or for the cure, mitigation, or treatment of any disease or condition. It does not replace a healthcare professional’s judgment or clinical diagnosis.
References: 1. McKiernan FE, Berg RL, Fuehrer J. Clinical and radiographic findings in adults with persistent hypophosphatasemia. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(7):1651-1660. 2.Bianchi ML. Hypophosphatasia: an overview of the disease and its treatment. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(12):2743-2757. 3. Kishnani PS, Rockman-Greenberg C, Rauch F, et al. Five-year efficacy and safety of asfotase alfa therapy for adults and adolescents with hypophosphatasia. Bone. 2019;121:149-162. 4. Adeli K, Higgins V, Nieuwesteeg M, et al. Biochemical marker reference values across pediatric, adult, and geriatric ages: establishment of robust pediatric and adult reference intervals on the basis of the Canadian Health Measures Survey. Clin Chem. 2015;61(8):1049-1062. 5. ARUP Laboratories. Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes, serum or plasma. Accessed March 30, 2023. https://ltd.aruplab.com/Tests/Pub/0021020 6. Rockman-Greenberg C. Hypophosphatasia. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2013;10(suppl 2):380-388. 7. Bishop N, Munns CF, Ozono K. Transformative therapy in hypophosphatasia. Arch Dis Child. 2016;101(6):514-515. 8. Colantonio DA, Kyriakopoulou L, Chan MK, et al. Closing the gaps in pediatric laboratory reference intervals: a CALIPER database of 40 biochemical markers in a healthy and multiethnic population of children. Clin Chem. 2012;58(5):854-868.


| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 10.6 | High | |
| Protein, g/dL | 6.5 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.6 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 63 | ||
| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.8 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 6.9 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.9 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 35 | ||
| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 10.2 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 7.1 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.0 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 32 | ||
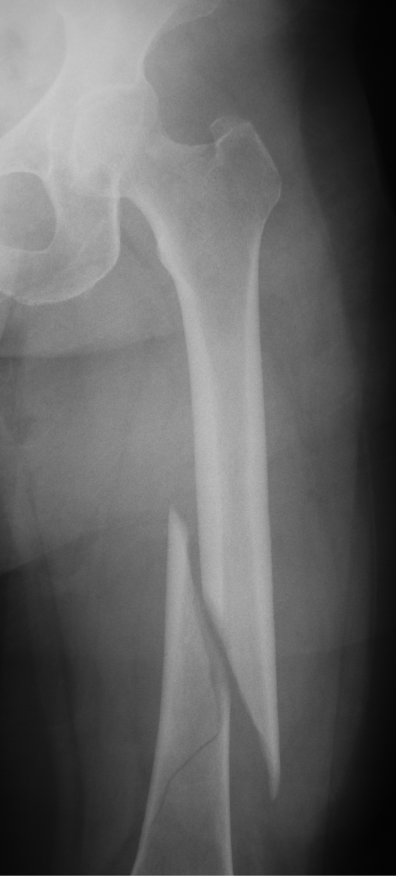
Femur fracture
age 13
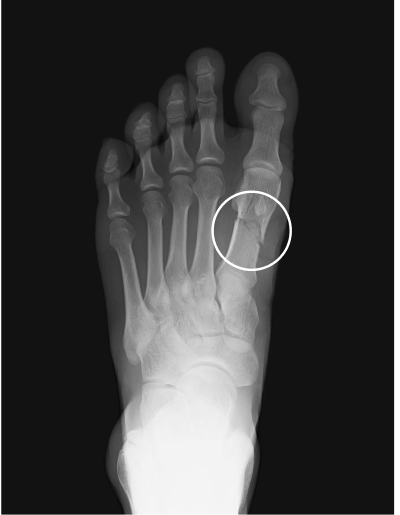
Metatarsal fracture
age 16
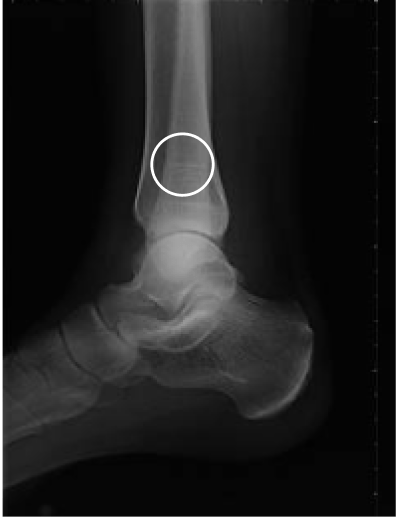
Tibial fracture
age 57


| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.9 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 7.1 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.1 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 34 | ||
| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.8 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 7.5 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 29 | ||
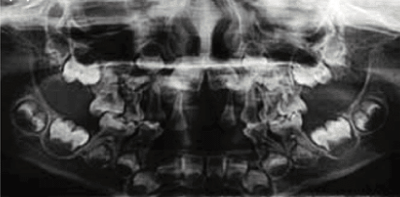
Radiograph showing enlarged pulp chambers and shape abnormalities.
Dental manifestations of hypophosphatasia in children and the effects of enzyme replacement therapy on dental status: A series of clinical cases by Larisa Kiselnikova is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
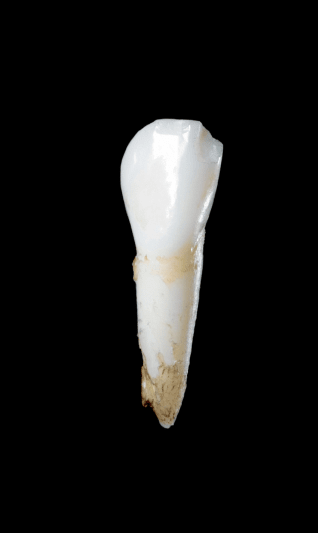
Early loss of baby teeth with root intact


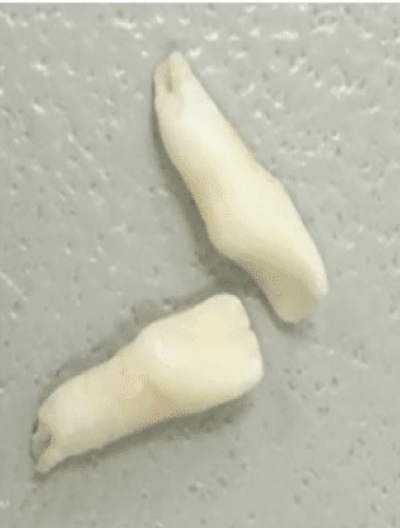
Nontraumatic tooth loss at age 4
Dental manifestations of hypophosphatasia in children and the effects of enzyme replacement therapy on dental status: A series of clinical cases by Larisa Kiselnikova is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.3 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 7.9 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 138 | ||
| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 9.1 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 8.1 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 130 | ||
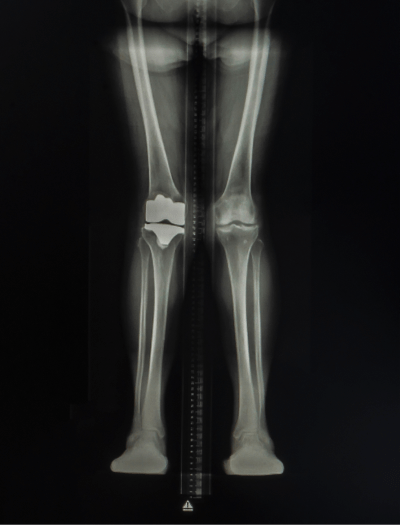
Currently presents with mild knock knees
Mild knock knees

Nontraumatic tooth loss at age 4
Dental manifestations of hypophosphatasia in children and the effects of enzyme replacement therapy on dental status: A series of clinical cases by Larisa Kiselnikova is licensed under CC BY 4.0.


| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 10 | ||
| Protein, g/dL | 7.1 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.9 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 93 | ||
| TEST | RESULT | FLAG | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium, mg/dL | 10.6 | High | |
| Protein, g/dL | 7.5 | ||
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.2 | ||
| Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L | 87 | ||

Profiles are based on hypothetical patient cases.
Nathan, 57
Profiles are based on hypothetical patient cases.
Medical History
Family History
Presenting Symptoms
Current Medications
Lab Results/Imaging
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
10.6
6.5
4.6
63
High
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
9.8
6.9
3.9
35
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
10.2
7.1
4.0
32
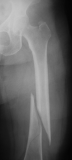
Femur fracture
age 13
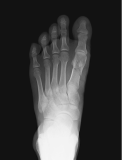
Metatarsal fracture
age 16

Tibial fracture
age 57
Physician Notes


Anna, 35
Profiles are based on hypothetical patient cases.
Medical History
Family History
Presenting Symptoms
Current Medications
Lab Results/Imaging
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
9.9
7.1
4.1
34
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
9.8
7.5
4.2
29

Delayed eruption of permanent teeth
Radiograph showing enlarged pulp chambers and shape abnormalities.
Dental manifestations of hypophosphatasia in children and the effects of enzyme replacement therapy on dental status: A series of clinical cases by Larisa Kiselnikova is licensed under CC BY 4.0.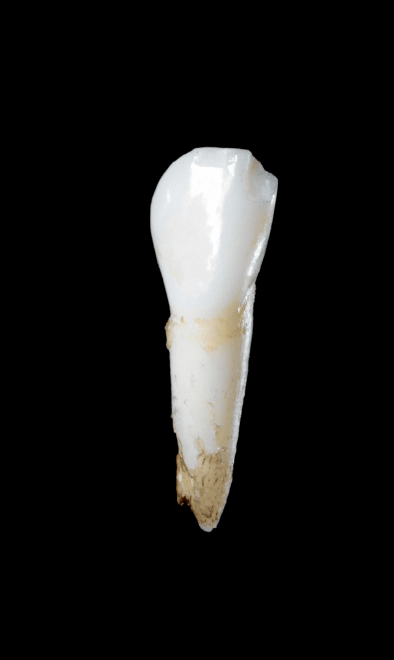
Early loss of baby teeth with
root intact
Physician Notes


Hannah, 7
Profiles are based on hypothetical patient cases.
Medical History
Family History

Nontraumatic tooth loss at age 4
Dental manifestations of hypophosphatasia in children and the effects of enzyme replacement therapy on dental status: A series of clinical cases by Larisa Kiselnikova is licensed under CC BY 4.0.Presenting Symptoms
Current Medications
Lab Results/Imaging
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
9.3
7.9
4.2
138
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
9.1
8.1
4.2
130

Currently presents with
mild knock knees

Nontraumatic tooth
loss at
age 4
Dental manifestations of hypophosphatasia in children and the effects of enzyme replacement therapy on dental status: A series of clinical cases by Larisa Kiselnikova is licensed under CC BY 4.0.
Physician Notes


Sarah, 7 months
Profiles are based on hypothetical patient cases.
Medical History
Family History
Presenting Symptoms
Current Medications
Lab Results/Imaging
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
10
71
3.9
93
Calcium, mg/dL
Protein, g/dL
Albumin, g/dL
Alkaline phosphatase, IU/L
10.6
7.5
4.2
87
High

Physician Notes


We use cookies to give you the best online experience. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.




